How to play like Dave Brubeck (Take 5 “steps”) – Brubeck’s sheet music available from our Library
Browse in the Library:
Search Posts by Categories:
Dave Brubeck, who passed away on December 5, 2012, just a day shy of his 92nd birthday, was one of the most influential jazz musicians of all time. Rhythms of horses’ hooves on the California cattle ranch he grew up on, along with those from water pumps, motors, and various other sources prompted his lifelong fascination with odd time signatures. Brubeck was also exposed to Bach, Mozart, Chopin, Beethoven, Debussy, and Ravel, as his mother gave classical piano lessons. Stride, blues, swing, bebop, classical, big block chords, and delicate counterpoint are just some of Brubeck’s signature devices. Let’s “take five” of them for a closer look. . . .

1. Blues
Many of Brubeck’s classic compositions were based on blues progressions, like “Sweet Cleo Brown,” a tribute to one of his great inspirations, blues singer Cleo Brown. Similarly, his solos were often infused with riffs drawn from the blues scale. Ex. 1 is a progression Brubeck typically used to end a blues.
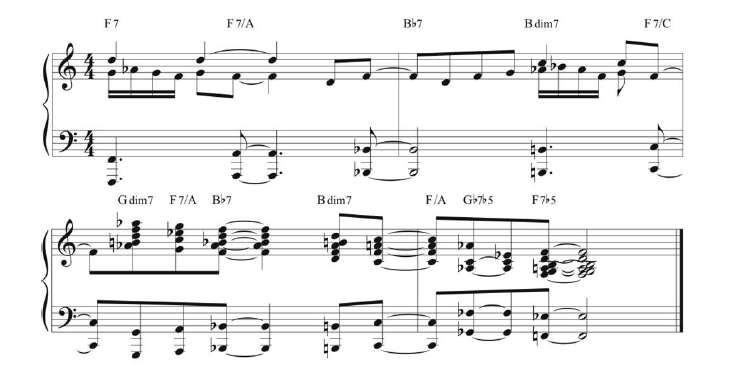
2. Stride
Some of Brubeck’s heroes were renowned for stride piano, like Duke Ellington, Earl “Fatha” Hines, Fats Waller, and Art Tatum. Brubeck’s large hands let him span big block chords with his right hand while playing
wide walking tenthswith his left. “It’s a Raggy Waltz” combines elements of stride and ragtime in 3/4 time— one of his first forays into non-4/4 time signatures. Playing in 3/4 also let him superimpose another pulse
over the beat—a polyrhythm—as in Ex. 2.

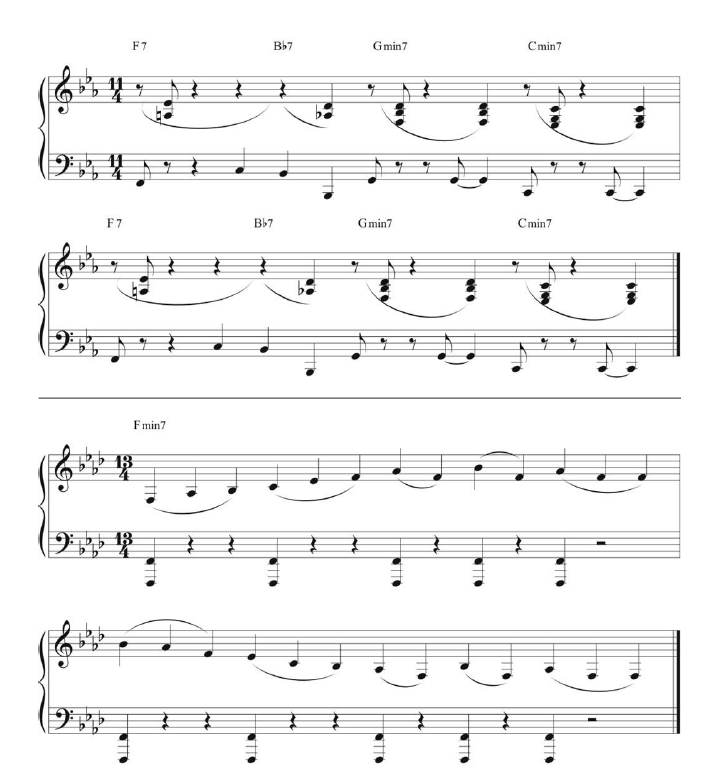
3. Odd time signatures
Brubeck once famously stated, “I don’t think jazz should be in 4/4 time.” His use of metric subdivisions—seen here marked in groups—was the secret ingredient that made odd time signatures sound natural and swinging to the causal listener. These broke up the measure into more digestible rhythmic phrases of (usually) two or three notes. For example, “Take Five” is more accessible when you count its 5/4 time as “one two three, one two.” Exs. 3athrough 3e (left to right) illustrate this approach in various time signatures.
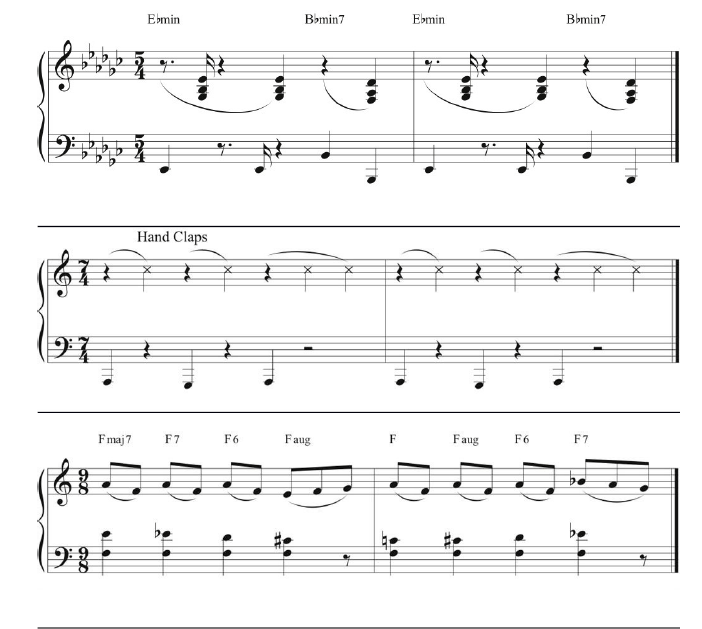

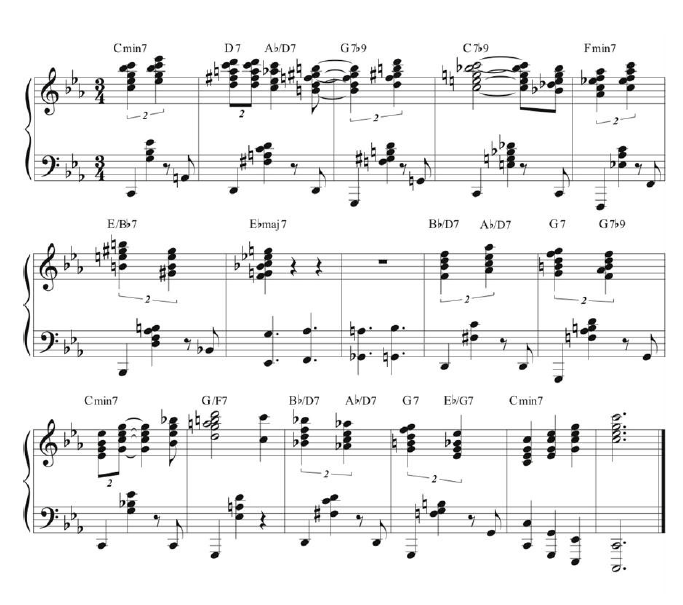
4. Polyrhythms
Ex. 4 demonstrates Brubeck’s renowned use of polyrhythms, or playing in more than one rhythm at a time. The rhythmic grouping of five notes in the place of four is distributed between two hands, a technique that’s been picked up by such pianists as Herbie Hancock and Chick Corea.

5. Polytonality
It was Brubeck’s older brother Howard, chairman of the music department at Palomar Junior College, who first suggested he study with French composer Darius Milhaud. During those studies, Brubeck began experimenting with polytonality—playing in more than one tonality at a time. While Brubeck is well known for his frequent display of fast pyrotechnics and dense textures, Ex. 5 exemplifies his use of space and openness.
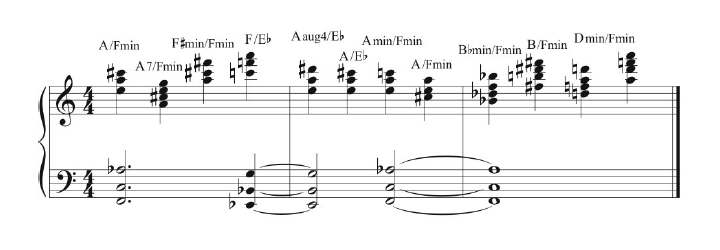
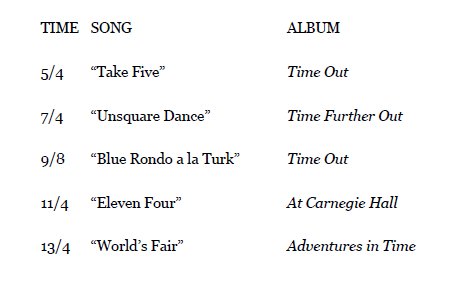
Signature Tunes
New to Brubeck? Here’s some required listening for getting to know his use of odd time signatures.
Dave Brubeck – Take Five
Paul Desmond (alto sax), Joe Morello (drums), Eugene Wright (bass) and Dave Brubeck (piano)
Paul Desmond (alto sax), Joe Morello (drums), Eugene Wright (bass) and Dave Brubeck (piano)
New Dave Brubeck Biography, A Timely Reminder Of Jazz Piano Royalty
‘Dave Brubeck: A Life In Time’ looks at how the pianist’s life criss-crossed with countless jazz greats, and dives into some lesser-known areas of his life.
Pianist David Warren Brubeck was born on 6 December 1920, in Concord, northeast of Oakland, and his centenary year is being recognised with an excellent, impressively detailed biography by Philip Clark (Dave Brubeck: A Life In Time, Da Capo Press), which explores the life and work of the musician, who died in 2012.
Clark spent time on the road with Brubeck and his wife, Iola, in 2003 and the biography contains fascinating new material about a man who pushed the boundaries of jazz for six decades, influencing scores of popular music stars, including Ray Davies of The Kinks, Ray Manzarak of The Doors and Deep Purple’s Jon Lord.
Sharp as a tack
Brubeck’s life criss-crossed with countless talented contemporaries and A Life In Time contains a wealth of information about his touring partner Miles Davis (who recorded Brubeck’s song ‘In Your Own Sweet Way’ back in 1957), along with Cecil Taylor, Chet Baker, Shelly Manne, Art Blakey, Lee Konitz, Charlie Parker, Cal Tjader, Lennie Tristano, Jimmy Giuffre, Max Roach and Gerry Mulligan, with whom Brubeck recorded an entire album.
The magnificent ‘Time Out’ and ‘Blue Rondo À La Turk’, both recorded in 1959, brought the Dave Brubeck Quartet international stardom – and they remain two jazz tunes that can be instantly recognised by members of the general public rather than diehard fans.
There are interesting offbeat reminiscences in the biography. Brubeck tells the author that the controversial comedian Lenny Bruce used to babysit his son Darius (who also became a jazz musician) after the musician and comic appeared on the same bill at the Crescendo club in Hollywood. “Lenny and I became good friends,” said Brubeck. “I didn’t expect Lenny and Darius to get close, but they kind of gravitated toward each other and we thought, Well, OK, it’s fine with us if someone wants to take the kids off our hands for the afternoon. And Lenny took it very seriously and was completely responsible, I have to say.”
Compared to the drug-taking excesses of some of his fellow jazz men, Brubeck seemed deeply conventional, but he was as sharp as a tack. He is quoted warning about gangsters who “worm their way past your defences”, adding that “Charlie Parker’s a sad example of what could happen” when people exploit the addictions of musicians.
Defiant in the face of racism
There are tales of Brubeck’s groundbreaking tours in the late 50s – he went to Poland and caught dysentery in Baghdad – and a moving account of his defiant attitude towards racism during an era of segregation. In 1960 he cancelled a promotional appearance on NBC’s hugely popular Bell Telephone Hour Show because the producers insisted that black bass player Eugene Wright would have to be out of shot.
In 1964, Brubeck also openly defied the Ku Klux Klan at a gig held at the systematically racist University Of Alabama. Brubeck insisted that the band and audience be integrated – and he defied threats of violence and disruption from the KKK to play the concert to a mixed audience. The stand forced the university to allow integrated concerts from then on.
Two giants of jazz – Duke Ellington and Louis Armstrong – come out well in the book. Brubeck admired Armstrong and wrote a musical for him called The Real Ambassadors. Brubeck could not get word direct to the famous trumpeter so waited outside his Chicago hotel room to ask him to take part in a production of the show.
“Eventually a waiter turned up with a tray of food, and when Louis opened and saw me there, he gave me a big smile and told the waiter that Mr Brubeck would be having the same as him – so one more steak, please,” the pianist recalled.

Armstrong happily agreed to the project, a matter of lasting pride to Brubeck, who had grown up admiring the trumpeter as well as pianists such as Fats Waller and Teddy Wilson, who were Satchmo’s contemporaries.
A move into composing
Though Brubeck is associated with Colombia Records, A Life In Time tells the fascinating story of his move to Decca Records – and why he chose to move to that famous label in 1968 to record his extended choral and orchestral albums The Light In The Wilderness and The Gates Of Justice. “Now that Brubeck was interested in pursuing a career as a composer, he felt that Columbia had let him down,” writes Clark.
Some of the music Decca recorded was composed by Brubeck in tribute to his nephew Philip, who had died from a brain tumour at 16. Columbia executive Teo Macero was upset to lose one of their top jazz stars, but he admitted in a company memo in October 1968 that Decca were “doing more” for Brubeck as a label – and talked wistfully about the merits of Blue Note and Verve in the jazz field.
Brubeck went on composing, recording and performing for the next four decades before dying on 5 December 2012, a day before his 92nd birthday, on the way to a cardiology appointment. He left a magnificent jazz legacy that is well served by Clark’s impressive book.
Dave Brubeck: A Life In Time, by Philip Clark, is published on 18 February 2020 by Da Capo Press in the US and Headline in the UK.
