- Thelonious Monk’s Harmony, Rhythm, and pianism (Part 3)
- Read Part 1 here and Part 2 here.
- Rhythm and Pianism
- Rhythm
- Pianism
- Analysis of Two Peers
- Find and download Thelonious Monk’s sheet music transcriptions in our Library.
- Thelonious Monk With John Coltrane (1961) (Full Album)
Thelonious Monk’s Harmony, Rhythm, and pianism (Part 3)
Read Part 1 here and Part 2 here.
Rhythm and Pianism
Rhythm
The rhythmic traits for which jazz is known and at which it excels—groove, swing, speed, heat, cool, polyrhythm, conversational interaction among players, dense and irregular improvised motives and phrases, antiphonal call and response, and more—are all but absent in ISC. Most modern jazz group performance emphasizes strict periodicity with terrific forward momentum created by players’ rhythmically propulsive contributions. Formidable mastery, poise, and virtuosity are needed to play.
Tempi are characteristically either fast enough to scare off would-be pretenders, or, just as daringly, cooled off to an unruffled “ballad” speed, and steady in either case. The metric backbone is the succession of harmonies with the beat usually actualized and propelled by the walking quarter notes of the bass and the drums’ “ride” cymbal. Though harmonies change on measure downbeats and sometimes middles, the beats in between—beats and in a four-beat measure—are stressed to create a driving backbeat.
Solo performances and recordings are almost exclusively the provenance of pianists, who could use the left hand to simulate the roles of the rhythm section, with either walking bass lines or the evocation of earlier styles such as stride or boogie-woogie. Monk himself made extensive use of these latter techniques on his own solo records, as well as on the unaccompanied numbers that were generally included in his live sets. Solo performers such as Art Tatum would also “extemporize,” straying from steady time in introductions, quasi-cadenzas, and so on. For Monk, though, a solo ballad like ISC was an opportunity to stretch time in a far more radical manner, eschewing steady time almost completely.
Swing, an idiomatic variation of the timing of the subdivided beat, depends on underlying regularity. It involves a dynamic relationship between measured periodicity and the realm of unmeasured music, rhythmic freedom that can be implied through soloists’ styles. This dynamism in turn references a melodic vernacular—the sense that a soloist is “speaking through their horn.” Some would argue that this has to do with the lyricism of the human voice, others that it represents some kind of middle ground between a discursive, rhetorical European way of making music and a more interactive, poly-rhythmic African approach. Others might say that both are true or that it simply feels good, and that, having been discovered and developed at the turn of the twentieth century, it proved irresistible.
Monk’s ISC can be said to swing only in the colloquial sense of being compellingly musical, that is, simply because he is saying something in a distinctive way. But strictly understood, swing can exist only against a conception of steady time, and in this recording nothing keeps time.
Except fleetingly in a few spots, it is impossible to move the body in any regular pulsation to Monk’s playing. He is clearly not keeping steady time internally—or else he has a very different clock. If we listen intently for the regularity most bodies crave—and which we expect from familiarity with more standard versions of the song—we must jolt in and out of time with him. The slow regular beat of the tune’s harmonic progression remains impassively present, a law both obeyed and mocked. Monk often played solo ballads in this manner, a meditation with outbursts, with an affect both reverent and ironic. In live performance with a group, this number would be surrounded by tunes that swung hard. In other words ISC’s rubato is heard—and is meant to be heard—in terms of the absence of jazz’s most authentic rhythmic traits, and of Monk’s abandonment of them in the service of other qualities.
Pianism
One of the most ergonomic inventions in human history, the piano and its eighty-eight-key action are among jazz’s essential European legacies. Its technology has empowered musical cultures as distant as Burmese and African American to adapt it to their own idioms, extending out from the panoply of European approaches to the instrument on completely unforeseen trajectories. Jazz piano’s trajectories crisscross and meld into a great tradition of their own.
No one gains entrance into the pantheon of jazz pianism without a strongly identifiable voice on the instrument. The differences among pianists are bread and butter to jazz lovers, from earlier era virtuosi like Jelly Roll Morton, James P. Johnson, Fats Waller, Earl Hines, and Art Tatum through beboppers like Bud Powell and Mary Lou Williams and on to a diversity of post-bop players far too numerous to cite or describe. But, as we have said, even among these names Monk comes in at a different angle due to a tightly bound combination of pianistic idiosyncrasies, harmony, and rhythm.
Yet we cannot properly appreciate these elements outside the context of what his peers developed for the instrument.
Keyboard concept, technique, and historical currents conspire to shape pianists’ approaches. All pianists have to consider multiple aesthetic issues determining what kinds of textures to favor in developing a style.
Individual tunes suggest their own approaches, but players develop idioms that carry over from tune to tune. Voicings can be played with from one to ten fingers—or sometimes, in Monk’s case, with flattened palms. Overall motion can be dense or sparse. The hands can be independent or interdependent. One can move freely around the entire keyboard or stay closer to its more conventional, “vocal” center. Nuances of touch, phrasing, and dynamic are essential.
Piano styles also group historically. The “orchestral” ways of playing that developed in jazz’s first few decades were strongly influenced by brass band marches and ragtime, and by the fact that before World War II jazz was primarily dance music. Pianists of those years tended to provide a clear beat and full harmonic support. Some, like bandleader Count Basie, favored economy of notes and texture. In contrast, there was nothing in piano technique or harmony that Art Tatum could not execute astonishingly, nor did he hesitate to infuse most everything he played with the encyclopedia of approaches at his disposal, in all kinds of combinations and throughout the entire range of the keyboard.
Bebop was for listening, not dancing, and its speed an excuse for cutting—that is, outplaying and stumping cohorts. The competition nudged piano technique to become lighter, fleeter, and sparser. The walking bass and drums safeguarded the time so pianists needed to do less in that regard, and the bass register was to some degree forsaken. Bud Powell’s style often rested on a chassis of insistent, rhythmically irregular, somewhat grating left-hand “shells” (the root of the chord played in the bass register, plus the seventh directly above it). Jutting from below, they cut in under single-line right-hand melodies that looped around the upper two-thirds of the keyboard, equaling Charlie Parker’s saxophone lines in their density and irregular phrasing.
In the 50s, jazz cooled off, tributaries of eclectic styles blossomed, and it became necessary to know how to play in many ways. Red Garland could imitate the fast-moving close harmonies of big band saxophone sections in passages featuring thick, parallel, two-handed chords moving with melodic gestures. Wynton Kelly emphasized idiomatic blues riffs. Influences of Cuban and Brazilian styles, and of modern European composition, gradually took root. But in the main, Powell’s saxophone-like approach to the right hand prevailed, while in the left hand many developed harmonically richer voicings, deployed somewhat like Powell’s shells.
Analysis of Two Peers
Compare figure 4.4’s transcriptions of the opening of I Should Care as played by Oscar Peterson and Bill Evans, two strikingly different but equally iconic pianists of the time. Peterson, stylistic and technical heir to Tatum, plays solo here with mid-range voicings of up to eight notes, some with left-hand shells, most containing all triad tones and the seventh. As mentioned earlier, he doubles the harmonic rhythm to quarter-note speed, which allows interpolation of tritone substitution dominants preparing the V and the I chords of mm. 1-2. The Eb7 at m. 1, beat 4 is voiced with a pungent #9 in addition to the seventh chord itself. Peterson exploits the hidden presence of an F# major triad within this sonority, playing it with the right hand to separate it from the Eb major triad
Figure 4.4a. Opening measures of Oscar Peterson’s version of I Should Care (transposed to D from the original key of Bb). From Soul-O!; Oscar Peterson, solo piano.
Figure 4.4b. Opening measures of Bill Evans’s version of I Should Care (transposed to D from the original key of C). From How My Heart Sings!; Bill Evans, piano, Chuck Israels, bass, and Paul Motian, drums.
Figure 4.4a and 4.4b
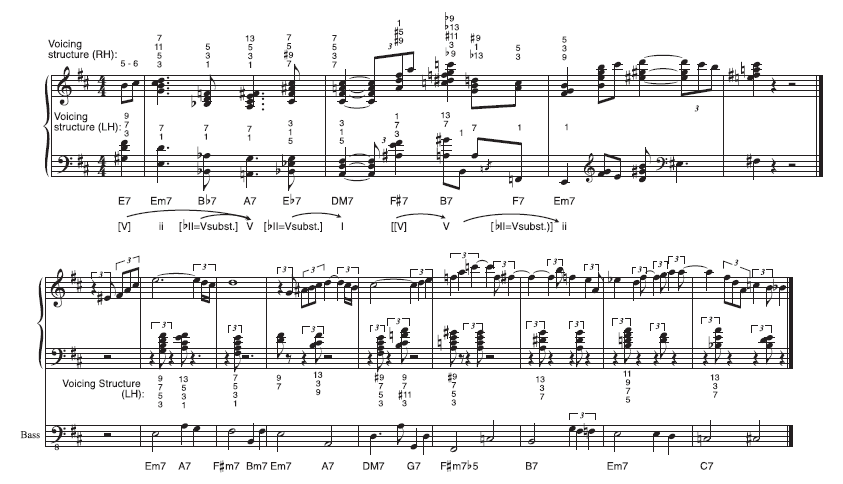
he places in the left. The left-hand triad then slides down in parallel motion to the downbeat of m. 2, but in the right the A# moves to A while the other tones remain in place. This reveals an F# minor triad comprising the third, fifth, and seventh of the DM7. The superpositions of triads and impeccable voice leading of this chord change are of a special richness in this region of the keyboard.
Shooting up in register, the F#7 chord on the second triplet eighth of m. 2, beat V is V of the B7 chord on beat 3, itself an applied V to the Em7 of m. 3. The F#7 is notable for its #9 (A) and the #5 (D), which is perhaps there only because Peterson has omitted the fifth of the chord (C# ; see also figure 4.3, middle column and second row under “Chromatic Tones”). On the next beat, where he brings the melody to a local peak, the fifth (F#) is again omitted, but both thirteenth (G#) and b thirteenth (G) are included. This B7, voiced with the root as an afterbeat, contains additional extension tones C and F that, combined with the others, conceal G# major, F major, C minor, and A diminished triads all at once. This sequence of lavish chords, texturally full and smooth, steady and propelled in rhythm and with a legato touch, give ISC sumptuous treatment.
Evans’s bass player Chuck Israels provides all the chord roots in metrically secure positions, so rather than double them or their rhythm, the pianist parries them with the left hand, playing deft offbeat rhythmic punches that converse polyrhythmically with the right hand’s intricate embellishment of the melody. Beyond this, however, Evan’s chord structures are similar to, albeit thinner than, Peterson’s. He remains in the piano’s central register, and he is equally fastidious about voice leading: the majority of the chord-to-chord connections proceed by step.
The elegantly contoured right-hand line begins by hugging the original tune, but transforms it completely after m. 4 (while still brushing the original C, B, and A in mm. 5-7). Evans sometimes uses melody to enrich the voicings, as when A–F# –D (thirteenth, #eleventh, ninth) is heard over the C7 chord in m. 8. He also gingerly clashes with them by using avoid tones, as with the F (#7) over the F#7b5 in m. 4, or the Eb similarly related to its Em7 harmony two measures later (see figure 4.3, left column and top row under “Chromatic Tones”). In both cases, though, Evans is careful to promptly lead by step to a more consonant resolution: the former moves up to F# at the end of the measure, while the latter goes directly down to D.
As we take up analysis of Monk’s ISC, we will find that features creating continuity in these two short excerpts—stepwise motion, propulsive rhythm, mid-range voicing, and a consistent level of density and dissonance—are missing. Monk did not by any means invent the notion of favoring discontinuities in these parameters. He did not come from nowhere, and it is well established that his style is part of a lineage extending from before Duke Ellington, through Monk, and on to later figures like avantgardist Cecil Taylor, not to mention the many who deliberately emulated Monk in recent decades. To hear those connections is a project for another time that would enable a crucial historical and stylistic narrative. But to frame Monk against the prevailing, more conventionally tasteful modern jazz aesthetics illustrated by figure 4.4 is to hear him at his most inimitable and strange.

Find and download Thelonious Monk’s sheet music transcriptions in our Library.
Thelonious Monk With John Coltrane (1961) (Full Album)
Browse in the Library:
| Artist or Composer / Score name | Cover | List of Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Verdi – Libiamo Ne Lieti Calici (La Traviata) (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Verdi – Va pensiero Piano Solo arr. NABUCCO ACTE III Choeur des ésclaves hébreux.mscz | ||
| Verdi La dona e mobile Rigoletto Piano Solo with lyrics |
 |
|
| Verdi La Dona E Mobile Rigoletto Piano Solo With Lyrics Musescore File.mscz | ||
| Verdi Requiem Cambridge Music Handbooks (Book) |
 |
|
| Vernon Duke Autumn In New York |
 |
|
| Vernon Duke – Autumn In New York (guitar arr. with TABs) |
 |
|
| Vertical Horizon – Best I Ever Had | ||
| Via con me (Paolo Conte) | ||
| Via del Campo (Fabrizio De Andrè) | ||
| Vianne Sets Up Shop (Chocolat OST) Rachel Portman | ||
| Vicente Amigo Ciudad De Las Ideas (Guitar TAB) |
 |
|
| Victor Herbert’s masterpiece Ah Sweet Mystery Of Life |
 |
|
| Victor Jara Un Canto Truncado Joan Jara (Book) Español – Spanish Biography – Biografía |
 |
|
| Victor Labenske Piano Miniatures 24 Short Solos In All Major And Minor Keys (Intermediate Piano) |
 |
Victor Labenske Piano Miniatures 24 Short Solos In All Major And Minor Keys (Intermediate Piano) |
| Victor Wooten Best of – transcribed by Victor Wooten Guitar Tabs |
 |
Victor Wooten Best of – transcribed by Victor Wooten Guitar Tabs |
| Victor Young When I Fall In Love |
 |
|
| Victor Young – Blue Star The Medic Theme |
 |
|
| Victor Young – Stella By Starlight Jazz Standard |
 |
|
| Victor Young – When I Fall In Love |
 |
|
| Victor young – When I Fall In Love Sheet Music as recorded by Celine Dion and Clive Griffin (fromm Sleepless in Seate) |
 |
|
| Victor Young (Bill Evans) – When I Fall In Love (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Victor Young And Peggy Lee Johnny Guitar |
 |
|
| Victor Young Around the World (piano solo sheet music) | Victor Young Around the World (piano solo sheet music) | |
| Victor Young Around The World In 80 Days Easy Piano Solo |
 |
|
| Victor Young Love Letters (Piano Solo arr.) |
 |
|
| Victor Young Stella by Starlight | Stella-By-Starlight-Victor-Young | |
| Victor Young Stella By Starlight Easy Piano Solo |
 |
|
| Victor Young Stella By Starlight Victor Young & Ned Washington Sheet Music 1946 Jazz Standard (Vintage sheet music) |
 |
|
| Vida Y Arte De Glenn Gould – by Bazzana Kevin (Español Spanish) |
 |
|
| Viktor Semenuita Suite The Spring Awakening for Guitar quartet |
 |
|
| Villa-Lobos – 12 Guitar Etudes (Doze Estudios para Violao) |
 |
|
| Villa-Lobos – Bachiana Brasileira no. 4 | ||
| Villa-Lobos – Bachianas Brasileiras No. 5 – Aria (Cantilena) partitura |
 |
|
| Villa-Lobos – Choros (N°1) Guitar Sheet Music (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Villa-Lobos – Prelude N° 3 (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Villa-Lobos -Etude №1 (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Villa-Lobos A Lenda do Caboclo | Villa-Lobos Lenda do Caboclo | |
| Villa-Lobos Five Preludes for Guitar, W419 |
 |
Wes Montgomery The Early Years (Mel Bay) Jazz Guitar Solos Tablature |
| Villa-Lobos Guia Patrico Album 2 | Villa-Lobos-GP-Album-2 | |
| Villa-Lobos Guia Patrico Album 3 | Villa-Lobos Guia Patrico Album 3 | |
| Villa-Lobos Prelude 1 for Guitar | Villa-Lobos prelude 1 | |
| Villa-Lobos Prelude No 1 (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Villa-Lobos Tristorosa Guitar arr. by Gorbunov |
 |
|
| Villa-Lobos, Heitor – Obras Completas (complete works for GUITAR) |
 |
Villa-Lobos obra completa guitarra |
| Villa-Lobos, Heitor – Aria (Cantilena) arr. for voice and guitar | Villa-Lobos, Heitor – Aria (Cantilena) arr. for voice and guitar | |
| Villa-Lobos, Heitor – Bachianas Brasileiras No 4 No 2 – Choral Song Of The Jungle | ||
| Villa-Lobos, Heitor – Saudades das selvas brasileras (pour piano) | Villa-Lobos – Saudades das selvas brasileras | |
| Vince Guaraldi A Charlie Brown Christmas |
 |
Vince Guaraldi A Charlie Brown Christmas |
| Vince Guaraldi Christmas Time Is Here |
 |
|
| Vince Guaraldi Linus And Lucy (Piano Solo) Peanuts Theme | Vince Guaraldi Linus And Lucy (Piano Solo) Peanuts Theme | |
| Vince Guaraldi – Cast Your Fate To The Wind | Vince Guaraldi – Cast Your Fate To The Wind | |
| Vince Guaraldi – Linus And Lucy (Piano Solo) Peanuts Theme (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Vince Guaraldi A Charlie Brown Christmas For Solo Jazz Guitar with TAB |
 |
Vince Guaraldi A Charlie Brown Christmas For Solo Jazz Guitar with TAB |
| Vince Guaraldi A Charlie Brown Christmast Beginning Piano Solos |
 |
Vince Guaraldi A Charlie Brown Christmast Beginning Piano Solos |
| Vince Guaraldi Collection 9 transcriptions |
 |
Vince Guaraldi Collection 9 transcriptions |
| Vince Guaraldi The Christmas Song |
 |
|
| Vince Guaraldi The Christmas Song (Mel Tormé and Robert Wells) Piano Solo | Vince Guaraldi The Christmas Song (Mel Tormé and Robert Wells) Piano Solo | |
| Vineyard Songbook (2011) Guitar Songchords |
 |
Vineyard Songbook (2011) Guitar Songchords |
| Vinicius De Moraes Vols 1,2 & 3 Guitar |
 |
Vinicius de Moraes 1,2 & 3 books |
| Vinnie Moore Masterclass (audio Mp3 Tab And Backing Track) GUITAR TABS and Al Di Meola Reh Video Booklet |
 |
|
| Violin Songs Big Book Of (Songbook) 130 songs |
 |
Violin Songs Big Book Of (Songbook) 130 songs |
| Virtuosity And The Musical Work The Transcendental Studies Of Liszt By Jim Samson Book |
 |
|
| Vittorio Monti Czardas (Piano Solo arr.) |
 |
|
| Vittorio Monti Czardas Piano violin arr. by J. Godderis |
 |
|
| Viva Italia Songbook A Travelogue In Song Piano Vocal Chordsby Curt Appelgren |
 |
Viva Italia Songbook A Travelogue In Song Piano Vocal Chordsby Curt Appelgren |
| Viva La Vida – Coldplay (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Vivaldi Largo Concerto D Guitar Arr |
 |
|
| Vivaldi Summer The Four Seasons Piano Solo Arr. | Vivaldi Summer The Four Seasons Piano Solo Arr. | |
| Vivaldi The Four Seasons (Piano Solo Arrangement) |
 |
|
| Vivaldi The Four Seasons Guitar arr. (A Suite of Themes) by Alxander Glüklikh |
 |
|
| Vivaldi Violin Concerto In F Major Op. 8 No. 3 Rv. 293 Autumn For Solo Piano | Vivaldi Violin Concerto In F Major Op. 8 No. 3 Rv. 293 Autumn For Solo Piano | |
| Vivaldi – Concert in G minor Summer arr. violin and piano |
 |
|
| Vivaldi – Concerto No. 2 In G Minor Op. 8 Rv 315mov. 3 Presto Summer L’estate Piano Solo Arr. (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Vivaldi – Concerto No. 2 in G minor, Op. 8, RV 315 mov. 3 Presto Summer L’estate Piano Solo arr. sheet music | Vivaldi – Concerto No. 2 in G minor, Op. 8, RV 315 mov. 3 Presto Summer L’estate Piano Solo arr. sheet music | |
| Vivaldi – Summer The Four Seasons Piano Solo arr..mscz | ||
| Vivaldi – Winter Guitar Arr. Based On Violin Concerto In F Minor Rv 297 L’inverno (Sheet Music) (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Vivaldi – Winter Guitar arr. based on Violin Concerto in F minor, RV 297 L’inverno (sheet music) | Vivaldi – Winter Guitar arr. based on Violin Concerto in F minor, RV 297 L’inverno (sheet music) | |
| Vivaldi Gloria Piano Reduction |
 |
|
| Vivaldi Master Musicians Series (Book) Biography by Michael Talbot |
 |
|
| Vivo Per Lei – Bocelli | ||
| Vivo per lei (Bocelli – Giorgia) | ||
| VK Vanros Kloud Wings Of Piano |
 |
|
| Vladimir Cosma Les Musiques De Films Vol 2 |
 |
Vladimir Cosma Les Musiques De Films Vol 2 |
| Vladimir’s Blues (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Volker Bertelmann – Lion Main Theme sheet music |
 |
|
| Volodos Mozart’s Turkish March From Sonata No. 11 |
 |
|
| Volodos – Rachmaninoff Where Beauty Dwells Melodiya Op. 21 No. 7 Version Putsmeiser Piano Solo |
 |
|
| Volumia – Afscheid | ||
| Volumia – Hou Me Vast | ||
| Vorrei (Lunapop) | ||
| W.C. Handy The St. Louis Blues | W.C. Handy The St. Louis Blues | |
| W.C. Handy – The St. Louis Blues (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| W.E. – Evgenis Waltz Abel Korzeniowski |
 |
|
| Wagner – Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg – complete (arr. for piano solo & voice) | Wagner – Die Meistersinger… | |
| Wagner – Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg -Vorspiel (arr. 2 for pianos) | Wagner – Die Meistersinger…Vorspiel | |
| Wagner – Die Walküre Ride of the Valkyries (arr. 2 for pianos) | Wagner – Die Walküre | |
| Wagner – Isoldens Liebestod For Two Pianos | ||
| Wagner – Parsifal – Entrance into the Castle of the Holy Grail (arr. piano) | ||
| Wagner – Prélude To Lohengrin (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Wagner – Prélude to Lohengrin (piano solo arr.) |
 |
|
| Wagner – Ride of the Valkyries – piano solo arr. | Wagner Ride of the Valkyries | |
| Wagner – Ride of the Valkyries (Piano solo) | Wagner – Ride of the Valkyries (Piano solo) | |
| Wagner – Ride Of The Valkyries (Piano Solo) (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Wagner – Tannhäuser Pilgrims Chorus – Richard Wagner Piano Solo with guitar Chords |
 |
|
| Wagner – Tristan und Isolde – Isoldes Liebestod (arr. piano solo) |
 |
|
| Wagner – Tristan und Isolde Prelude & Isoldes Liebestod (arr. for 2 pianos) | Wagner – Tristan und Isolde | |
| Wagner Ouverture Thanhauser (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Wagner Siegfried’s Funeral March From Götterdämmerung (Piano Solo) (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Wagner Tannhauser Piano Solo arr. | Wagner Tannhauser Piano Solo arr. | |
| Wagner-Busoni – Funeral March (Il Crepuscolo degli Dei) arr. piano solo |
 |
Wagner-Busoni Funeral March |
| Wagner, Richard TANNHÄUSER Piano solo arr. J. Doebber |
 |
|
| Waiss Elena Andante From Mi Amigo El Piano (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Waiss, Elena Mi Amigo El Piano |
 |
|
| Waitress (The Musical) – Opening Up Sara Bareilles (Voice and Piano) |
 |
Waitress sheet music |
| Walking In The Footsteps Of Paul Chambers (Bass technique) |
 |
Walking In The Footsteps Of Paul Chambers |
| Walt Disney Pictures Intro (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Walter Carroll Tunes From Nature First Piano Lessons Easy Pieces For Beginners (Vintage sheet music) |
 |
|
| Walter Kent – White Cliffs Of Dover | ||
| Waltz – Boston (Alexander Rozenbaum) |
Alto Saxophone – Gigi Gryce (# A3, B2)…. Bass – Wilbur Ware (# A1 to B2)…. Drums – Art Blakey (#A3, B2), “Shadow” Wilson (#A1, A2, B1)…. Piano – Thelonious Monk…. Tenor Saxophone – Coleman Hawkins (# A3, B2), John Coltrane…. Trumpet – Ray Copeland (# A3, B2)…. ……………………………………………… A1 Ruby, My Dear 0:00 A2 Trinkle, Tinkle 6:22 A3 Off Minor 13:03 B1 Nutty 18:19 B2 Epistrophy 24:58 B3 Functional 28:09 ……………………………………………… Recorded – New York; 1957-58.
