Thelonius Monk‘s sheet music transcriptions are available from our Library.
Chords and Voicings: From Lead Sheet to Performance
In modern jazz, seventh chords specified by lead sheets may appear simply as shown in figure 4.2a, but musicians rarely follow what the lead sheet specifies to the letter. Well before Thelonious Monk came on the scene, jazz pianists vied to distinguish themselves with ingenious voicings. A kind of common practice prevailed in bebop, though we emphasize that musicians can and did step outside this practice in search of particular expressions and logics. In the main, though, four complementary techniques developed, two concerning voicing as such and two concerning chord choice—what chord to play where:
Voicing
• Extension and omission: addition of tones foreign to the chord proper, and/or dropping tones that are part of it
• Spacing and doubling: distribution of a voicing on the piano or among instruments in an ensemble.
Harmonic choice
• Substitution: replacement of one chord by another with equivalent function
• Insertion and deletion: increase or decrease in the rate of harmonic motion by adding to or subtracting from changes specified on the lead sheet.
Extension, omission, spacing and doubling
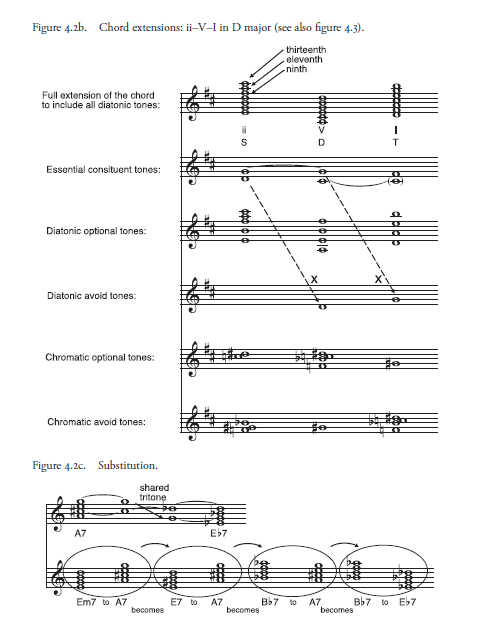
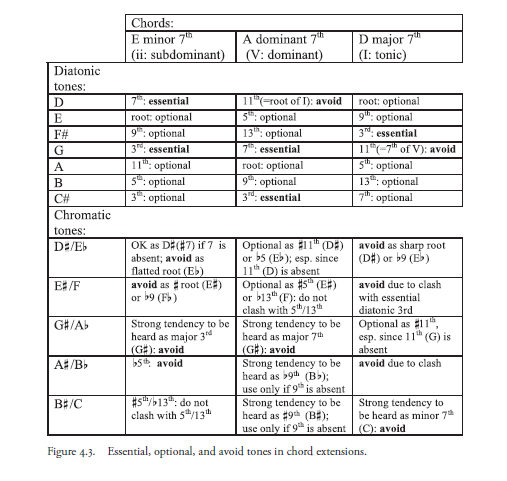
Figures 4.2b and 4.3 illustrate possibilities for extending minor seventh, dominant seventh, and major seventh harmonies, and apply them to the initial ii–V–I of ISC. In the first staff each chord is extended upward by thirds beyond the seventh to include the ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth above the root. Each of the resulting seven-note stacks of thirds includes all notes of the D major scale. The fact that all three chords extend through the exact same pitch collections, in the same intervallic arrangement (i.e., a stack of thirds), demonstrates the fundamental role that harmonic function—and not chord or voicing—plays in determining tonal meaning in jazz.
The chords could in some cases even be voiced in identical ways, but their functional context would make them heard and understood differently. Here is a significant way in which, it seems to us, jazz harmony differs in emphasis from European practice.
To the extent that the distinction between ii, V, and I voicings blurs, what is it precisely that distinguishes their functions? The second staff shows which of the seven diatonic tones are directly involved in the progression toward and away from the V chord’s tritone.
Typically, these tones are necessary and sufficient to convey harmonic function. Surprisingly for anyone familiar with European harmony, neither the fifth nor the root of the chord are necessary; indeed these may be dropped (and possibly supplied by a bass player, but not necessarily). But in order to convey function and quality most effectively, the essential tones are typically arranged in the lower register of the voicing, with extension tones higher up.
The third staff of figure 4.2b distills the optional diatonic tones, which may be used without diluting function or quality, and the fourth staff shows how the tonic note (D) and the fourth scale step (G) are carefully avoided in the dominant and tonic chords, respectively, so as not to carry them over from the chords that precede them, which would impede the ii–V–I motion (see dashed arrows).
Outside the diatonic pitch collection remain fi ve tones completing the chromatic aggregate, which can provide rich “upper structures” to voicings. In some cases these work against important diatonic intervals; for example, using a G with the Em chord could obscure the minor third between E and G; using it with the A7 chord would weaken the C#/G tritone. But with the DM7 it sounds all right because its diatonic “shadow,” G, is already avoided. Figure 4.3 sketches the effect of chromaticism in each chordal context.
All optional diatonic and chromatic tones may be withheld or used, and they may be spaced from low to high in limitless ways. Attention is paid to the choice of lowest pitch, the registers of all others, thickness (number of notes played at once), and the use of some pitches in more than one octave doubling. This topic is discussed later in reference to specifi c instances in short excerpts by pianists Bill Evans and Oscar Peterson (figures 4.4a and b), and also at length in relation to Monk.
Chord Substitution, Insertion, and Deletion
Because every dominant-quality seventh chord shares its tritone with the dominant-quality seventh chord whose root is a tritone away, the chords in each such pair may be substituted for one another ( figure 4.2c, first staff).
Substitutions for V are idiomatic in ii–V–I motion. In D major, this turns Em7–A7–DM7 into Em7–Eb7 –DM7 and causes the roots to descend chromatically by half step rather than by fifth, an especially characteristic marker of modern jazz sound. The second staff of figure 4.2c illustrates another kind of substitution, involving change of chord quality. In the first stage, the ii of
the ii–V–I progression is intensifi ed by raising its third from G to G# . This makes it E7, a dominant seventh chord, that is, V7 in relation to the A7 chord, and thus “tonicizes” the root of A7 as if A were momentarily the home key. From here it is a matter of applying the tritone substitution principle just discussed to convert the pair of chords into progression from Bb7 to Eb7. Monk does just this in ISC ( figures 4.1 and 4.5 , mm. 15-16).
Harmonic rhythm is the rate at which harmonies change. A scan of the various versions of ISC in figure 4.1 shows chords changing usually every two or four beats, though Oscar Peterson achieves special intensity in mm. 1-2 by changing on each beat, and there are scattered instances of chords held longer. Since harmony’s depth of field is rich, even with these severe constraints on harmonic rhythm there can be infinite ways to realize the harmonies in a song and suggest unexpected aural routes through it.
Sometimes root progressions by fifth are concatenated, as in figure 4.1, staff 2, mm. 2-3. Here, rather than have mm. 3-4 be a repetition of mm. 1-2, as it is in Monk’s version (staff 3), the ii chord of m. 3 is treated as a local tonic and preceded by its own ii–V. The two new bass tones F and B are part of the D major scale, so the motion feels activated but the connections do not jar.
The major third (D#) of the B7 chord is the only chromatic alteration implied. In Bill Evans’s version, the bass player faithfully provides the root tones (figure 4.4b), but Evans does not reflect the change on the piano. Without the D#, the feeling of tonicization is absent, and we have labeled the chord as Bm7.
Earlier we mentioned a more deeply hued insertion, at mm. 8 and, which introduces a ii–V (Gm7 to C7) progression borrowed from F major, a key built on a tonic foreign to the D major scale. This motion is so distinctive that it might be heard as one of the strongest markers of the song as a whole. In the fake book version, after slipping momentarily toward F in this way the music slips right back to DM7 in m. 9.
Monk, however, reinterprets the C7 as a tritone substitution for an F#7, and resolves in m. 9 to Bm7 (the fake book does this too, but later, at the parallel moment in mm. 25). Another insertion in the fake book version, reflecting a mix of diatonic and chromatic moves, comes at the final measures (31-2).
This characteristic “turnaround” revs up the motion, propelling the music toward the next repetition of the form. Monk’s seeming extension of this passage and the two prior measures reflect a musical action we shall describe later; in figure 4.1 we condense his chords into the thirty-two-measure form (the actual measure numbers cor-responding to mm. 29-38of the transcription in figure 4.5 are shown below the lowest staff).
Deletions put the brakes on chord progression. In this idiom they are somewhat rarer than insertions but noteworthy for that reason. When Monk slows down the fake book chords at m. 2 he wants to focus on the very repetition of the chord progression in the initial two pairs of measures, and when he does it again at mm. 15-16 it is as if we are asked to savor the tritone substitutions selected for those moments.
Modern jazz harmonic practice often seems to be founded on the intensifi cation and complexifying of its diatonic basis in the several ways we have just described all at once—so the instances in which this process is slowed or impeded provide a special repose.

Browse in the Library:
| Artist or Composer / Score name | Cover | List of Contents |
|---|---|---|
| A dozen A Day Book 1 Technical exercises for the piano |
 |
A dozen A Day Book 1 Technical exercises for the piano |
| A dozen A Day Book 2 Technical exercises for the piano |
 |
|
| A dozen A Day Book 3 Technical exercises for the piano |
 |
|
| A dozen A Day Book 4 Technical exercises for the piano |
 |
|
| A dozen A Day Mini Book Technical exercises for the piano |
 |
|
| A dozen Day Preparatory Book Technical exercises for the piano |
 |
|
| A Farewell To Arms Love Theme From A Farewell To Arms film by Mario Nascimbene Francis Webster 1957 |
 |
|
| A Felicidade (Antonio Carlos Jobim) | ||
| A Festival Gathering Of Carols (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| A Fine Frenzy – Almost Lover |
 |
|
| A Fistful of Dollars (Ennio Morricone) | ||
| A Generative Theory Of Tonal Music by Fred Lerdahl and Ray Jackendoff (Book) |
 |
|
| A Guide To Guitar Chords by Curt Sheller |
 |
A Guide To Guitar Chords by Curt Sheller |
| A Guide To Musical Analysis by Nicholas Cook (Book) |
 |
|
| A Handbook Of Piano Playing (By Eric Hope) (1962) |
 |
|
| A Heart Full Of Love (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| A love suicide (Yutaka Minobe) | ||
| A Love Supreme (by Ashley Kahn) The story of john Coltrane’s signature album (Book) |
 |
|
| A Media Luz (Edgardo Donato) | ||
| A Modern Approach To Jazz Rock And Fusion For Guitar with Tablature |
 |
A Modern Approach To Jazz Rock And Fusion For Guitar |
| A Modern Method For Guitar (Berklee) 1 by William Leavitt |
 |
A Modern Method Berklee 1 |
| A Modern Method For Guitar (Berklee) 2 by William Leavitt |
 |
A Modern Method For Guitar (Berklee) 2 |
| A Modern Method For Guitar (Berklee) 3 by William Leavitt |
 |
A Modern Method For Guitar (Berklee) 3 |
| A MOZART REINCARNATED (Ennio Morricone) |
 |
|
| A Mozart Reincarnated by Ennio Morricone (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| A New Approach To Ear Training by Leo Kraft (BOOK) |
 |
|
| A New Approach To Piano Technique (By Ruth A. Dickerson) (1962) |
 |
A new approach to piano technique |
| A Night In Tunisia – Dizzy Gillespie.mscz | ||
| A Pedal Method For The Piano (By Albert F Venino) (1893) |
 |
|
| A Popular Account Of Ancient Musical Instruments And Their Development by William Lynd (Book 1897) |
 |
|
| A Rockin’ Christmas Piano Vocal Guitar |
 |
20 songs to sing on a rockin’ Christmas Eve Includes: All I Want for Christmas Is You * Grandma Got Run Over by a Reindeer * Happy Xmas (War Is Over) * Jingle-Bell Rock * Merry Merry Christmas Baby * Rockin’ Around the Christmas Tree * Santa Baby & moreRockin Christmas |
| A Single Man – George’s Waltz (Shigeru Umebayashi) | ||
| A Single Man – Stillness of the Mind (Abel Korzeniowski) | ||
| A Smooth Jazz Christmas – Mellow Seasonal Favorites for Piano arr. Roger House |
 |
A Smooth Jazz Christmas – Mellow Seasonal Favorites for Piano arr. Roger House |
| A Song For You – Leon Russell Ray Charles (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| A Star Is Born – Always Remember Us This Way Lady Gaga |
 |
|
| A Star Is Born – Shallow Lady Lady Gaga |
 |
|
| A Tale Of Two Sisters Ost – Epilogue Piano Solo |
 |
|
| A Thousand Years – Twilight OST (Christina Perri) | ||
| A Time For Love – Johnny Mandel |
 |
|
| A Time For Us – Guitar TABlature |
 |
|
| A Time For Us (Love Theme from Romeo and Juliet) Nino Rota |
 |
|
| A Time For Us (Romeo and Juliet OST) Nino Rota | ||
| A Touch Of Jazz 14 well-known hymns, gospel songs and contemporary praise songs by Wolaver Bill |
 |
A Touch Of Jazz 14 well-known hymns, gospel songs and contemporary praise songs by Wolaver Bill |
| A Tribute To Ella Fitzgerald Piano Vocal Guitar |
 |
A tribute to ELLA FITZGERALD |
| A Walk To Remember – Only Hope | ||
| A whiter shade of pale – Procul Harum | A whiter shade of pale – Procul Harum | |
| AaRON U-turn Lili Piano |
 |
|
| Ab Ovo – Joep Beving (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Abba – Abba Gold – Greatest Hits |
 |
ABBA Gold Geatest Hits booksong sheet music |
| Abba – Chiquitita | ||
| Abba – Dancing Queen | ||
| Abba – Fernando | ||
| Abba – I Have A Dream | ||
| Abba – Like An Angel Passing Through My Room | ||
| Abba – Mamma Mia | ||
| Abba – Slipping Through My Fingers | ||
| Abba – Thank You For The Music | Abba-Thank-You-For-The-Music 1st page | |
| ABBA – Thank You For The Music (Piano Vocal Guitar) | ABBA – Thank You For The Music (Piano Vocal Guitar) | |
| ABBA – Thank You For the Music (Piano vocal Guitar) (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Abba – Thank You For The Music Piano & vocal | Abba – Thank You For The Music-abba-satb | |
| Abba – The Winner Takes It All | ||
| ABBA Dancing Queen Easy Piano Solo |
 |
|
| ABBA Fernando (Piano Solo arr.) |
 |
|
| ABBA Fernando (Piano Solo arr.).mscz | ||
| ABBA Greatest Hits |
 |
ABBA GREATEST HITS SHEET MUSIC BOOK |
| ABBA I Have A Dream |
 |
|
| Abba The Very Best Vol 1 Easy Piano Hans Gunter Heumann Pop Classics For Piano |
 |
Abba The Very Best Vol 1 Easy Piano |
| Abba The Very Best Vol 2 Easy Piano Hans Gunter Heumann Pop Classics For Piano |
 |
Abba The Very Best Vol 2 Easy Piano |
| Abbey Lincoln Songbook |
 |
Abbey Lincoln Songbook |
| Abbey Lincoln Songbook Piano Vocal Guitar Chords |
 |
Abbey Lincoln Songbook Piano Vocal Guitar Chords |
| Abdullah Ibrahim – The Piano World Of |
 |
Abdullah Ibrahim, The Piano World Of |
| Abdullah Ibrahim The African Piano Of Abdullah Ibrahim Vol 1 |
 |
Abdullah Ibrahim The African Piano Of Abdullah Ibrahim Vol 1 |
| Abdullah Ibrahim The Wedding (piano solo transcription sheet music, partition) |
 |
|
| Abel Korzeniowski – Death Is My Heir (from Romeo and Juliet) |
 |
|
| ABRSM Jazz Piano Pieces Grade 1 to 5 |
 |
ABRSM Jazz Piano Pieces Grade 1 to 5 ABRSM Jazz Piano Pieces Grade 5ABRSM Jazz Piano Pieces Grade 5 |
| ABRSM Piano Exam Pieces Grade 1 (2016) |
 |
ABRSM Piano Exam Pieces Grade 1 (2016) |
| ABRSM Piano Scales, Arpeggios Grade 8 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Piano Scales, Arpeggios and broken chords Grade 1 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Piano Scales, Arpeggios and broken chords Grade 4 |
 |
ABRSM Piano Scales, Arpeggios and broken chords Grade 4 |
| ABRSM Piano Scales, Grade 2 A Guide for Students and Teachers | ABRSM Piano Scales, Grade 2 A Guide for Students and Teachers | |
| ABRSM – Time pieces for guitar vol. 1 |
 |
|
| ABRSM – Time pieces for guitar vol. 2 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 1 |
 |
ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 1 |
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 2 |
 |
ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 2 |
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 3 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 4 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 5 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 6 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 7 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2017 18 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 8 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 1 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 2 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 3 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 5 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 6 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Grade 8 |
 |
|
| ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Initial Grade |
 |
ABRSM 2021-2022 Piano Exam Pieces Initial Grade |
| ABRSM Aural Training In Practice Book 1 Grades 1 to 3 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Aural Training In Practice Book 2 Grades 4 and 5 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Discovering Music Theory (Complete) Grades 1 to 5 Workbook by Simon Rushby (2020 Exams) |
 |
ABRSM Discovering Music Theory (Complete) Grades 1 to 5 Workbook by Simon Rushby (2020 Exams) contents |
| ABRSM Erster Verlust Grade 4 ABRSM Piano Exam Pieces 2021 & 2022 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Etude In A Minor – Dmitry Kabalevsky ABRSM Grade 4 Piano Exam Pieces 2021 & 2022 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Grade 2 – Inter-City Stomp byChristopher Norton From Microjazz Collection (Sheet Music) |
 |
|
| ABRSM Initial Grade Piano Exam Pieces 2023 2024 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Minuet and Trio D 41 No 21 – Franz Schubert ABRSM Grade 4 Piano Exam Pieces 2021 & 2022 |
 |
|
| ABRSM More Music Theory Sample Papers Grade 5 For New Format |
 |
|
| ABRSM Music Theory In Practice, Grade 1 (Eric Taylor) |
 |
|
| ABRSM Music Theory In Practice, Grade 2 (Eric Taylor) |
 |
|
| ABRSM Music Theory Past Papers Grade 1 2004 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Music Theory Past Papers Grade 4 2016 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Music Theory Past Papers Grade 5 2012 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Music Theory Past Papers Grade 6 2013 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Nikki Iles Danny Boy ABRSM Piano Exam Grade 8 2023 Jazz Piano arr. inspired by Bill Evans |
 |
|
| ABRSM Nikki Iles Friends Book 1 Intermediate Jazz Pieces For Piano |
 |
ABRSM Nikki Iles Friends Book 1 Intermediate Jazz Pieces For Piano |
| ABRSM Nikki Iles Friends Book 2 Intermediate To Advanced Jazz Pieces For Piano |
 |
ABRSM Nikki Iles Friends Book 2 Intermediate To Advanced Jazz Pieces For Piano |
| ABRSM Nikki Iles The Elephant Parade ABRSM piano Exam |
 |
|
| ABRSM Piano 2025-2026 Grade 8 C3 A Nightingale Sang in Berkeley Square by Sherwin – Maschwitz |
 |
|
| ABRSM Piano Exam 2007-2008 Grade 3 |
 |
|
| ABRSM Piano Exam 2015-16 Grade 3 |
 |
ABRSM Piano Exam 2015-16 Grade 3 |
