Table of Contents
Béla Bartók: Analysis of his music 1. (sheet music available)
Tonal Principles
The Axis System
“Every art has the right to strike its roots in the art of a previous. age; it not only has the right to but it must stem from it”, Bartok once declared.
His tonal system grew out of functional music. An uninterrupted line of evolution can be followed from the beginnings of functional . concepts, through the harmonies of Viennese classicism and the tone-world of romanticism to his axis system.
Best Sheet Music download from our Library.
By an analysis of his compositions, this axis system can primarily be shown to possess the essential properties of classical harmony, i.e.
(a) the functional affinities of the fourth and fifth degrees
ibr the relationship ofrelative major and minor keys
(cd _the overtone relations
( d) the role ofleading notes
.ei the opposite tension of the dominant and subdominant (/) the duality of tonal and distance principles
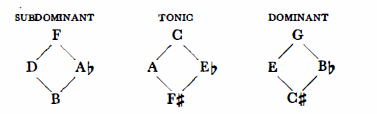
(a)To begin with, let us try to situate Bartók’s tonal system in the circle of fifths, Let us take C as the tonic (T). Then F, the fourth degree, is the subdominant (S); G, the fifth degree, ia the dominant (D); A, the sixth degree and relative of the tonic, functions as a tonic; D, the second degree, and relative of the subdominant, functions as a subdominant; E, the third degree and relative of the dominant, functions as a dominant. The series of fifths, F-C-G-D-A-E corresponds to the functional series S-T-D-S-T-D.
Please, subscribe to our Library.
If you are already a subscriber, please, check our NEW SCORES’ page every month for new sheet music. THANK YOU!
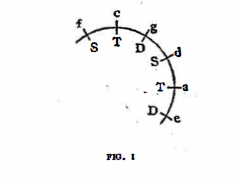
We note that the sequence S-T-D repeats itself. When this periodicity is extended over the entire circle of fifths the scheme of the axis system may be clearly seen:
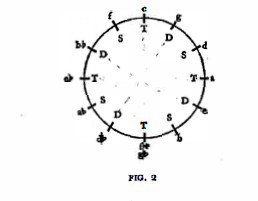
Let us separate the three funtions and call them tonic, subdominant dominant and dominant axes, respectively.
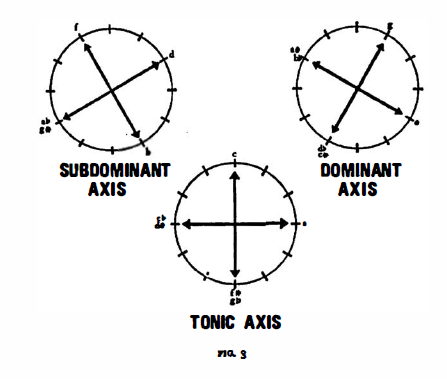

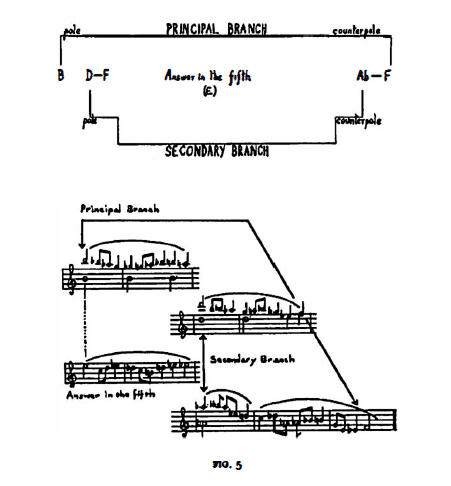
This table teaches yet another lesson. All four movements rest on the tonic axis, A-C-Eb-F#. Thus the first and fourth movements are supported by the “principal branch”, A and Eb,; the middle movements, however, by the “secondary branch”, C and F#, Thus each axis has a two-fold affinity depending on whether we oppose the pole with the counterpole, or the principal branch with the secondary branch.
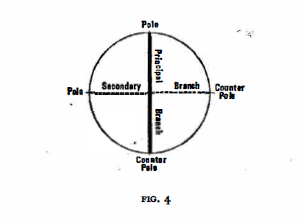
Consequently the components of the axis system are as follows:

The Slow Movement of the Sonata for Two Pianos and Percussion is based on the subdominant axis, B-D-F-Ab, complying with the traditions of classical composition. The modal arrangement of its principal theme is symmetrical: the beginning and end supported by the B and F counterpoles (i.e. the principal branch of the axis).
b) A survey of the evolution of harmonic thinking leads to the
conclusion that the birth of the axis system was a historical
necessity, representing the logical continuation (and in a _<:ertain sense the completion) of European functional music. It can be demonstrated that the axis system, with its characteristic features had, in effect, been used by the Viennese “Greats”. Indeed, it had been recognised by Bach, in his chromaticism.
The sense of functional correlation in music was introduced in practice by the realisation of the I-IV-V-I affinity (in medieval modal music, at first in cadence form only) In the case of the C tonic:
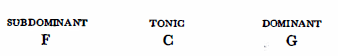
The classical theory of harmony already speaks of primary and secondary triads inasmuch as the C may be replaced by its relative A, the F by its relative D and the G by its relative E.
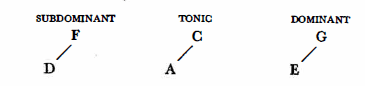
Romantic harmony goes still further, making frequent use of the upper relatives. (Naturally only major and minor keys of similar key signature may be regarded as relatives, e.g. C major and A minor, or C minor and Eb major):
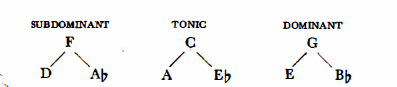
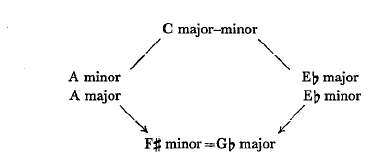
One more step completes the system. The axes extend the application of relatives to the whole system. The axis system implies the recognition of the fact that the common relative for A and Eb, is not only C, but also F# ( =Gb); that D and Ab, not only have F as a common relative, but also B; and that E and Bb, not only have G, but also C# ( =Db) as common relatives.
As is well known, Bartók showed a preference for the use ofso-called majoMninor chords (see Fig. 32b). For instance, its form in C tonality is:

The function remains unchanged even if the C major modeas shown in the above chord-is replaced by the relative A minor, or when the Eb major tonality replaces the relative C minor. This technique occurs regularly in Bartók’s music:
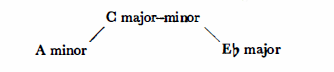
These substitute chords may also be employed in major-minor form, which brings the system to a close, since the relative of A major (F# minor) and that, of Eb, minor (Gb major) meet at a point of enharmonic co.incidence, F#=Gb.
These relatives, applied to dominant and subdominant harmony, again result in the scheme of the axis system.
(c) The theory of the axis system is also substantiated by the laws of acoustics. Acoustically, arriving from the dominant to the tonic, is to reach the root from an overtone-all cadential relations rest on the principle of interconnection between roots and their overtones. Thus, the dominant of C is not only G but also the next overtones E and Bb. Therefore the circle of tonic-dominant relationships is expanded to include E-C and Bb-C.
Since the D-T relationship corresponds relatively to
the T-S and
the S-D relationship,
overtone-root attraction exists between the T-S and the S-D, as well.
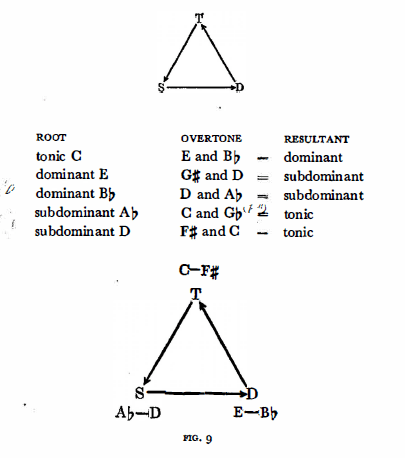
If we add the role of the nearest overtone, i.e. the fifth, then we
can deduce the complete axis system from these relations.
(d) In the simplest cadence, that of V7-I, the main role is played by the so-called sensitive notes which produce the pull of the dominant towards the tonic. The leading note pulls to the root and the seventh towards the third degree of the tonic, i.e. the leading note B resolves on C ind the seventh F on E or Eb.
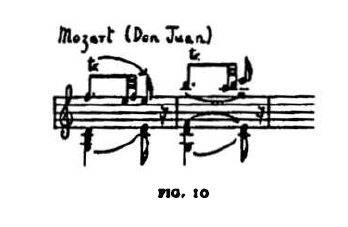
These important sensitive notes bear a tritonic relationship to each other. The tritone–half the octave interval-is characterised by the interchangeability of its notes without changing the interval. Thus, if the B-F relationship is converted into an F-B one (as is frequently the case with Bartók), then the F ( =E#) assumes the role of the leading note, pulling towards the F# instead of E, while the seventh B pulls towards A# or A instead of C. So, instead of the expected tonic C major, the counterpole, the equally tonic F# major (or minor) emerges.

This resolution is reserved by Bartók for a sudden change of scene. The circumstances of an expected G7-C cadence emerging as G7-F# gives us a “Bartokean pseudo-cadence”.
(e) Starting from the tonic centre C we reach the dominant in one direction and the subdominant in the other, in identical latitudes. At a distance of i fifth we find the dominant G upwards and the subdominant F downwards. Regarding overtone relations we also get the dominant G, E, Bb, in the upper and the subdominant F, Ab, D the lower directions.
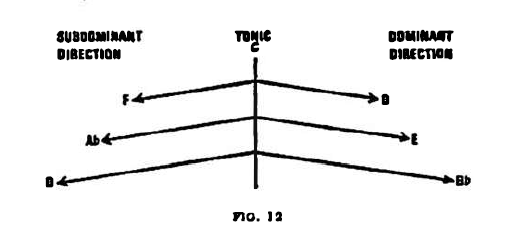
But what happens if the pendulum covers the latitude of a tritone? In this case the deviations made upwards and downwards meet, both ending at F# ( =Gb), and ifwe were to take one as the dominant, then the other would have to assume the subdominant function. By this coincidence, however, a neutralisation of their functions takes place, dominant and subdominan t merging are rendered ineffective in the interaction of their opposite forces.
Consequently the balance is saved, and the function is invariably that of the tonic. The counterpole is born. Similarly the distance between the tonic C and F# is bisected by Eb ( =D#) in the one and by A in the other direction; so lying in tensionless, neutral section points, they also have to be interpreted as tonics,. No more than four tonic poles can be surmised, since the intervals C-Eb, Eb-F#, F#-A, A-C provide no further points of bisection.
Finally, what significance should be attached to a swing of a chromatic degree, of C-B and its counterpart C-C# (=Db,)? Which is then to assume the dominant and which the subdominant function? Related to B, C# shows a degree of elevation of two fifths, which might correspond to the S-D interdependence, but not to its opposite. Anyway, the subdominant function of B and the dominant function of C# are unquestionable when they are related to the tonic F# counterpole.
(f) Thus, observing the logic of functional interconnection of the three axes, another interesting point arises. The subdominant and dominant are represented most effectively not by the degrees IV and V but, in the case of C tonality, the subdominant by Ab, (and its counterpole), the dominant by E (and its counterpole).
This is, after all, nothing new since there is, for instance, the dominant secondary theme in E of Beethoven’s Waldstein Sonata (C major) or the subdominant Slow Movement in Ab, of the Pathetique (C minor). The movements of Brahms’ First Symphony have the following key-sequence: C-E-Ab,-C in the sense of tonic-dominant-subdominant-tonic, etc.
However, the above examination of the axis system fails to explain why Bartók prefers these augmented triad relations to the traditional I-IV-V-I.
This necessitates a new approach to the system.
It is generally accepted that twelve-tone music shows a strong tendency to indifferent tonal relations.
Atonal relations can be most suitably effected by the equal division of the octave, or of the circle of fifths. By dividing the octave m twelve equal parts we get the chromatic scale; in the case of six equal parts we have the whole-tone scale; four equal parts gives us the chord of the diminished seventh; three the augmented triad, and finally by dividing the octave into two equal parts we arrive at the tritone.
For the present we shall exclude the whole-tone scale because of its limited possibilities: two whole-tone scales produce the chromatic scale by interlocking.
Every tonal system presupposes a centre as well as subordinate relations dependent on the centre. Taking again C as the tonic centre, the three functions are represented most potently by those degrees dividing the circle of fifths into three equal parts, i.e. in the augmented triad C-E-Ab. Properties inherent in classical harmony are responsible for the E assuming a dominant function and Ab, a subdominant function in relation to the tonic C.
Each of these main notes permit their substitution by their counterpoles, i.e. their tritonic equivalents. Thus, C may be replaced by F#, E by Bb, and Ab by D.
If we divide the twelve-tone chromatic scale proportionally between the three functions, each function will have four poles, and these-insofar as we keep to the distance principle-are arranged in diminished-seventh relations, dividing the circle into four equal parts. Accordingly, C-Eb-F#-A belong to the range of the C tonic, E-G-Bb-C# to that of the dominant E main note, and Ab-B-D-F to that of the subdominant Ab, main note.
So, the tonal system resulting from a division of the chromatic scale into equal parts agrees completely with the axis system:
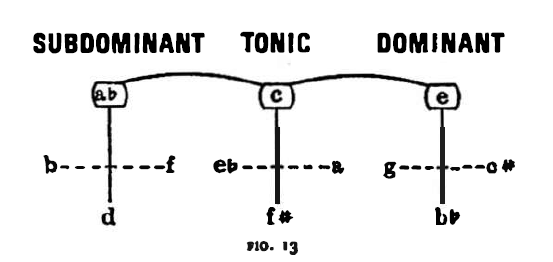
Put concisely, given the twelve-tone system and the three functions this is the on[y system that can be realised by means of distance division.
Viewed historically, the axis system reflects the age-old struggle between the principles-of tonaliry and equi-distance, with the gradual ascendancy of the latter which finally resulted in the free and equal treatment of the chromatic twelve notes.
Here we have to draw a line between Bartók’s twelve-tone system and the Zwölftonmusik of Schönberg. Schönberg annihilates and dissolves tonality whereas Bartók incorporates the principles of harmonic thinking in a perfect synthesis. To penetrate into Bartók’s creative genius is to discover the natural affinities and intrinsic possibilities, inherent in the musical material.
Béla Bartók Piano Sonata, Sz. 80 with sheet music
Browse in the Library:
| Artist or Composer / Score name | Cover | List of Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Bill Evans Blue In Green |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Interplay (Piano Solo Sheet Music Transcription) | Bill Evans Interplay (Piano Solo Sheet Music Transcription) | |
| Bill Evans Laurie |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Like Someone In Love Transcription From The Album Time Remembered (Sheet Music) | Bill Evans Like Someone In Love Transcription From The Album Time Remembered (Sheet Music) | |
| Bill Evans Waltz For Debby (Complete Version) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans When I Fall In Love Victor Young |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Time Remembered 14 Piano transcriptions |
 |
Bill Evans – Time Remembered 14 Piano transcriptions |
| Bill Evans – Alfie (Piano transcription) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Alice in Wonderland | Bill Evans – Alice in Wonderland | |
| Bill Evans – Autumn Leaves | Bill Evans – Autunm Leaves | |
| Bill Evans – Autunm Leaves (As Recorded by) | Bill Evans – Autunm Leaves (As Recorded by) | |
| Bill Evans – B minor Waltz (for Ellaine) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Blue in Green (Piano transcription) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Danny Boy, by Frederic Weatherly (Bill Evans Jazz version) | Bill Evans – Danny Boy, by Frederic Weatherly (Bill Evans Jazz version) | |
| Bill Evans – Emily Bass sheet music |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Ev’rything I Love (sheet music transcription) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Everything Happens to me – a musical biography by Keith Shadwick (Book) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Gone with the wind transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – In a Sentimental Mood – Piano solo transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Midnight Mood by Joe Zawinul | Bill Evans – Midnight Mood by Joe Zawinul | |
| Bill Evans – My Foolish Heart by Victor Young | Bill Evans – My Foolish Heart by Victor Young | |
| Bill Evans – My Funny Valentine (Transcription) Jazz Standard sheet music |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Never Let Me Go (Piano transcription) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Never Let Me Go (Piano Transcription) (Musescore File).mscz | ||
| Bill Evans – One for Helen | Bill Evans – One for Helen | |
| Bill Evans – Only Child transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Piano Solos |
 |
Bill Evans Piano solos |
| Bill Evans – Rare Transcriptions 3 | Bill Evans – Rare transcriptions vol. 3 sheet music | |
| Bill Evans – Rare transcriptions vol.1 | Bill Evans – Rare transcriptions vol.1 sheet music | |
| Bill Evans – Rare transcriptions vol.2 | Bill Evans – Rare transcriptions vol. 2 sheet music | |
| Bill Evans – Remembering The Rain.mscz | ||
| Bill Evans – Santa Claus Is Coming To Town |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Signature Licks – Piano Transcriptions |
 |
Bill Evans – Signature Licks – Hal Leonard – Piano Transcriptions |
| Bill Evans – Skating in Central Park (Solo) from Undercurrent with Jim Hall |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Someday My Prince Will Come from Portrait in Jazz sheet music Transcription | Bill Evans – Someday My Prince Will Come from Portrait in Jazz sheet music Transcription | |
| Bill Evans – Star Eyes (melody transcription) from The Universal Mind of Bill Evans | Bill Evans – Star Eyes (melody transcription) from The Universal Mind of Bill Evans (first page sample) | |
| Bill Evans – Star Eyes (melody transcription) from The Universal Mind of Bill Evans.mscz | ||
| Bill Evans – The 70’S Solo Piano |
 |
Bill Evans – The 70’S, Solo Piano |
| Bill Evans – The Artistry Of (Songs And Improvisation Transcription) |
 |
Bill Evans sheet music |
| Bill Evans – The Dolphin piano solo transcription | Bill Evans – The Dolphin piano solo transcription | |
| Bill Evans – The Dolphin Transcription sheet music |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – The Last Compositions |
 |
Bill Evans – The Last Compositions |
| Bill Evans – Theme From Mash |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Turn out the Stars | Bill Evans – Turn out the Stars_compressed | |
| Bill Evans – Turn Out The Stars – Bill Evans (Transcription) Jazz Standard sheet music (from Some Other Time) | Bill Evans – Turn Out The Stars – Bill Evans (Transcription) Jazz Standard sheet music | |
| Bill Evans – Very Early |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – Very Early Live In Paris [1972] solo transciption |
 |
|
| Bill Evans – We will meet again from The 70’S Solo Piano |
 |
|
| Bill Evans (1969) Emily sheet music transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans 4 New Versions Of Bill Evans Tunes Taken From His Recordings |
 |
Bill Evans_4 New Versions Of Bill Evans Tunes Taken From His Recordings |
| Bill Evans And The Craft Of Improvisation |
 |
Bill Evans craft improvisation |
| Bill Evans Autumn Leaves (as played in Portrait in Jazz) complete transcription | Bill Evans Autumn Leaves (as played in Portrait in Jazz) complete transcription | |
| Bill Evans But Beautiful transcription | Bill Evans But Beautiful transcription | |
| Bill Evans Collection For Solo Guitar |
 |
Bill Evans Collection For Solo Guitar |
| Bill Evans Emily |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Fake Book (60 original transcriptions) |
 |
Bill Evans Fake Book (60 original transc.) — Bill Evans Fake Book |
| Bill Evans Five |
 |
|
| Bill Evans How My Heart Sings – as played by Bill Evans | Bill Evans How My Heart Sings – as played by Bill Evans | |
| Bill Evans How My Heart Sings By Pettinger Peter (Book) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Jazz Piano Transcriptions |
 |
Bill Evans Jazz Piano Transcriptions |
| Bill Evans Jim Hall – Romain from Undercurrent |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Like Someone In Love sheet music transcription (1962 Sessions) | Bill Evans April Like Someone In Love sheet music transcription (1962 Sessions) | |
| Bill Evans Midnightmood |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Nardis (Bill Evans Trio) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Oleo (Transcription) | Bill Evans Oleo | |
| Bill Evans Omnibook For Piano Transcribed exactly from his recorded solos |
 |
Bill Evans Omnibook For Piano Transcribed exactly from his recorded solos |
| Bill Evans Perfect Piano Score |
 |
Bill Evans Perfect Piano Score |
| Bill Evans Piano Interpretations |
 |
Bill Evans-Piano Interpretations sheet music library |
| Bill Evans Piano Solo Transcriptions |
 |
Bill Evans Piano Solo Transcriptions |
| BILL EVANS Plays – Original Compositions Solo Transcriptions |
 |
Bill Evans Plays |
| Bill Evans Plays Duke Ellington Reflections In D |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Plays Standards |
 |
Bill Evans Plays Standards sheet music |
| Bill Evans Quiet Now (Jazz Standard) Transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Santa Claus Is Coming To Town Transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Solo Sessions Vol 1 Everything Happens To Me |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Solo Sessions Vol 2 What Kind Of Fool Am I |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Solo Sessions Vol1 April In Paris |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Songbook Jazz Piano Solos Series, Volume 19 (Bill Evans) |
 |
Bill Evans Songbook Jazz Piano Solos Series, Volume 19 (Bill Evans) |
| Bill Evans Stella By Starlight Jazz Standard The Bill Evans Trio Vol 2 Transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Tenderly Everybody Digs | Bill Evans Tenderly Everybody Digs | |
| Bill Evans The Bill Evans Trio Vol 1 |
 |
bill-evans-trio-Volume 1 1956-1961-transcriptions sheet music |
| Bill Evans The Bill Evans Trio Vol 2 |
 |
Bill Evans The Bill Evans Trio Vol 2 |
| Bill Evans The Bill Evans Trio Vol 3 |
 |
Bill Evans The Bill Evans Trio Vol 2 |
| Bill Evans The Mastery Of Bill Evans Artist Piano Transcriptions (a close look at two classic compositions: Waltz for Debby and Very Early) by Pascal Wetzel |
 |
Bill Evans The Mastery Of Bill Evans Artist Piano Transcriptions |
| Bill Evans Time Remembered (lead sheet) | Bill Evans Time Remembered | |
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of April, 1962 Sessions Danny Boy |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of April, 1962 Sessions Easy To Love |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of April, 1962 Sessions In Your Own Sweet Way |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of April, 1962 Sessions Like Someone In Love |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of Everybody Digs Peace Piece |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of New Jazz Conceptions Waltz For Debby |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of Solo Sessions Vol.1 Medley My Favourite Things, Easy To Love, Baubles, Bangles And Beads |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of Solo Sessions Vol.2 I Loves You, Porgy (Complete Transcription) |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of Solo Sessions Vol.2 Love Is Here To Stay |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of Solo Sessions Vol.2 Medley Autumn In New York, How About You |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcription sheet music of Solo Sessions Vol.2 Santa Claus Is Coming To Town |
 |
|
| Bill Evans Transcriptions (Own Tunes and tunes by Earl Zindars) |
 |
Bill Evans Transcriptions (Own Tunes and tunes by Earl Zindars) |
| Bill Evans Trio – Jazz improvisation (Transcriptions) |
 |
Bill Evans Trio – Jazz improvisation (Transcriptions) |
| Bill Evans Turn Out Star | ||
| Bill Evans We Will Meet Again |
 |
|
| Bill Evans When I Fall In Love |
 |
|
| Bill Evans You Go to my Head Piano solo (Omnibook For Piano Transcribed exactly from his recorded solos) Haven Gillespie J. Fred Coots | Bill Evans You Go to my Head Piano solo (Omnibook For Piano Transcribed exactly from his recorded solos) Haven Gillespie J. Fred Coots | |
| Bill Evans- Body And Soul Transcription |
 |
|
| Bill Frisell – St. Louis Blues Guitar Solo Transcription | Bill Frisell – St. Louis Blues Guitar Solo Transcription | |
| Bill Frisell An Anthology |
 |
Bill Frisell An Anthology |
| Bill Frisell Guitar Artisrty |
 |
Bill Frisell Guitar Artisrty |
| Bill Gaither Homecoming Souvenir Songbook |
 |
|
| Bill Haley Rock Around The Clock Bill Haley & The Comets Easy Piano Solo |
 |
|
| Bill Haley – Rock Around The Clock | ||
| Bill Holman Front Runner Full Band Score |
 |
|
| Bill Holman Kingfish Full band score |
 |
|
| Bill Holman Malaga – Full Big Band |
 |
|
| Bill Piburn plays Antonio Carlos Jobim – Jobim (Guitar with TABS) |
 |
Bill Piburn plays Antonio Carlos Jobim – Jobim (Guitar with TABS) |
| Bill Withers – Ain’t No Sunshine | ||
| Bill Withers – Lean On Me | ||
| Bill Withers Ain’t No Sunshine Piano Vocal Guitar |
 |
|
| Bill Withers Lovely Day |
 |
|
| Bill Withers Lovely Day Piano Vocal Guitar chords |
 |
|
| Billie Eilish Lovely With Khalid |
 |
|
| Billie Eilish Wish You Were Gay Lu |
 |
